Prof. Zhang Yongsheng's research group at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has systematically investigated the thermoelectric (TE) properties of three pyrite-type IIB-VIA2 dichalcogenides (ZnS2, CdS2 and CdSe2), and explored their physical mechanisms and several chemical trends.
Their findings were published in Physics Review B.
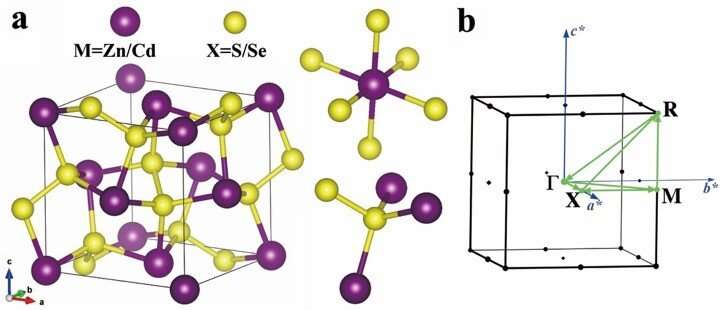
Through high-throughput computations, the three pyrite-type IIB-VIA2 dichalcogenides (ZnS2, CdS2, and CdSe2) with simple cubic structure and cheap elements had been predicted to possess promising TE properties by the team. However, the detailed TE behaviors and the fundamental underlying physical mechanisms behind them still remain ambiguous.
For this study, the researchers investigated the thermal and electrical transport properties of the three pyrite-type IIB-VIA2 dichalcogenides, and evaluated their thermoelectric performances taking advantage of more accurate methods.
After calculating and analyzing the phonon properties, they concluded that all three pyrite-type dichalcogenides had localized high-frequency optical phonons contributed by their strongly covalently bound nonmetallic dimers and soft phonon modes contributed by their rattling like metal atoms, which resulted in their strong anharmonicities and low thermal conductivities.
There are also chemical trends where heavier atomic masses, larger atomic displacement parameters and longer bond lengths between metallic and nonmetallic atoms may lead to softer phonon frequencies.
-
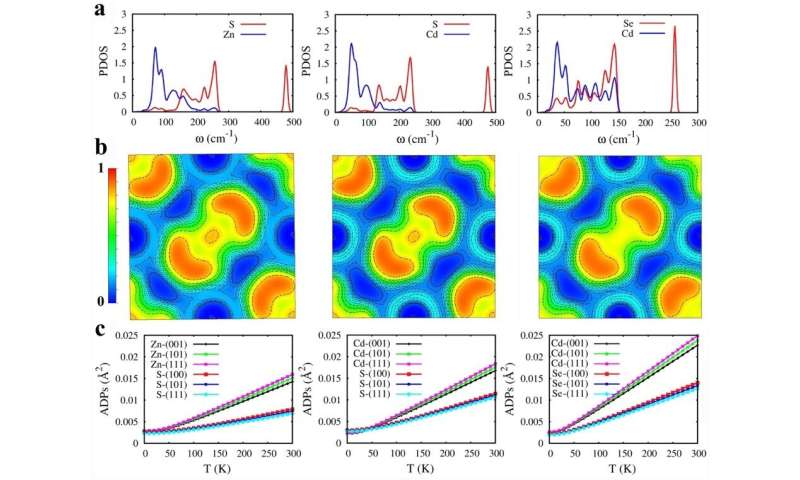
Figure 2. Calculated partial phonon densities of states. Credit: Jia Tiantian -
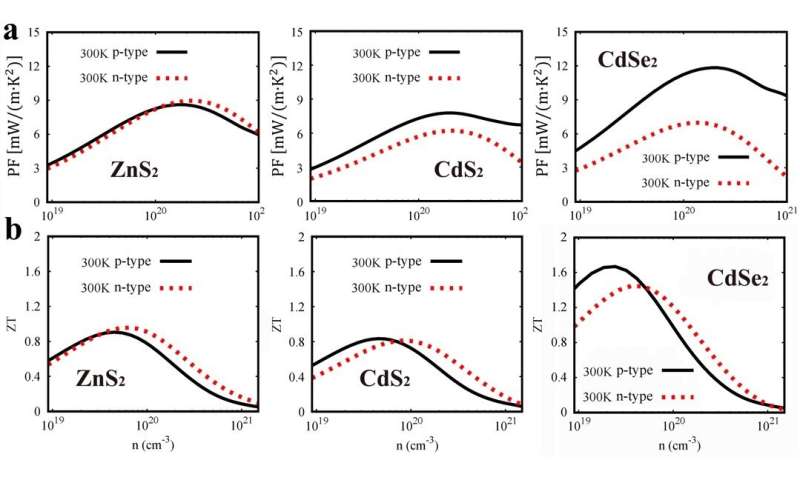
Figure 3. Calculated power factors (a) and figures of merit (b) as functions of the carrier concentration for p-type and n-type doping at 300 K in ZnS2, CdS2 and CdSe2 (from left to right), respectively. Credit: Jia Tiantian
Furthermore, all the three compounds showed promising electrical transport properties for both p-type and n-type doping due to their large density-of-states effective masses and small conductivity effective masses, which could be explained by the complex non-spherical iso energy Fermi surfaces in the valence and conduction bands.
Beyond that, they found the low lattice thermal conductivity and promising electrical transport properties contributed to their excellent thermoelectric performances.
"This study illustrates the effects of the localized nonmetallic dimers and the rattling-like metal atoms on the thermal transport properties, and the importance of different carrier effective masses to electrical transport properties in these pyrite-type dichalcogenides, which could be used to predict and optimize the TE properties of other TE compounds in the future," said Jia Tiantian, first author of the study.
Explore further
Citation: Chemical trends in high thermoelectric performance proved in pyrite-type dichalcogenides (2022, August 29) retrieved 29 August 2022 from https://ift.tt/FIpZA2r
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
"type" - Google News
August 29, 2022 at 08:01PM
https://ift.tt/FIpZA2r
Chemical trends in high thermoelectric performance proved in pyrite-type dichalcogenides - Phys.org
"type" - Google News
https://ift.tt/CBYLWwN
https://ift.tt/TVXFQ5S
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "Chemical trends in high thermoelectric performance proved in pyrite-type dichalcogenides - Phys.org"
Post a Comment